Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) are essential for the European Union’s (EU) economic growth and development. Accounting for over 99% of economic and social enterprises, SMEs contribute significantly to the EU’s GDP and employment. This article explores the significance of SMEs in EU funding policy and highlights their role in driving innovation, regional development, and job creation. It examines the support programs offered by Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe, emphasizing their focus on SMEs to promote sustainable growth and enhance the well-being of European citizens. The article concludes by underlining the continued importance of SMEs and their potential to foster a resilient and inclusive economy. So you want to know why and how EU countries support SMEs, then this study, examining the importance of SMEs in EU support policy, is available for you.
Dr. Saeid HAJIHASSANIASL, Cademix Institute of Technology.
Introduction
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) role in EU funding policy is important and vital. They are beneficial for the society and economy of the country for many reasons. If suitable conditions and fields are created, small and medium enterprises will be able to grow and develop. These enterprises play an important role in creating employment, providing a suitable platform for innovation and increasing exports. Since these companies have high flexibility, therefore more entrepreneurship and creativity takes place in them. So, paying attention to research and development expenditures in general and especially in such companies has special importance.
It is a fact that SMEs can react faster to economic factors. Also they employ more population and train skilled labor. The role of SMEs in EU Funding policy is important. They also play a significant role in the economy of the EU. According to statistics, SMEs include more than %99 of the economic and social enterprises of EU. This causes the development of effective programs and experiences in the field of SMEs in the EU. A very good literature has been developed in this field. In addition, the transition economies of Eastern Europe joined the EU and the diversity of the SMEs culture in these countries has prompted this union to develop funding programs. These programs align different definitions to the category of SMEs to undertake appropriate and efficient support programs in line with the improvement and development of SMEs.
In this study, the importance of SMEs and the role of research and development examined first, and then the support programs of Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe reviewed in order to support these companies.
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
Various definitions have been provided for SMEs. But in general, not very complicated industries with no require large investments to start are called small and medium-sized enterprises. These industries provides very benefits from an economic point of view. The growth of entrepreneurship, innovation, dynamism, creation of job opportunities and overall economic growth are among the their advantages.
Classification of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
The number of employees, the amount of assets, debts and the amount of annual turnover of companies are among the criteria for the division of these industries. Examining the number of people working in a company considered as one of the common classification standards in the world, but the size of this standard is also different in different countries.
According to the World Bank definition, micro enterprises have less than 10 employees. Their maximum annual income or sales is less than 100,000 dollars. Small businesses have also between 10 and 50 labor force. The maximum income of this type of business is between 100000 and 3 million dollars. Medium-sized enterprises have a maximum income of between 3 – 15 million dollars. In this category, the number of employee is between 50 – 300.
The numbers in the EU category shows somewhat different from the World Bank. However, in this category as well, the companies divide into three categories: micro, small and medium. In the first category, according to the EU definition, the number of people working in these enterprises is less than 10 employees. This enterprises have less than 2 million euros turnover. Less than 50 people work in small-size enterprises and their turnover is less than 10 million euros. Less than 250 people works in medium-size enterprises and their turnover is less than 50 million euros.
The Rationale behind the Focus on SMEs role on EU Funding Program
As an essential catalyst for innovation, competitiveness, and growth in Europe, SMEs are one of the main beneficiaries of European funding programs, particularly Horizon 2020 and the subsequent Horizon Europe. SMEs role in EU funding policy related to their innovation and competitiveness. This aims to enhance the impact of research and development (R&D) activities on the sustainability and overall well-being of European citizens.
- Economic Backbone: SMEs represent 99% of all businesses in the EU, contributing to 55% of its GDP and providing two-thirds of the total private sector employment in the EU (European Commission, 2020). They are the backbone of the EU economy, and investing in their growth directly promotes economic stability and prosperity.
- Innovation, Information Technology and Industrial Competitiveness Increase: SMEs play an important role in the process of technological change. They provide a significant source of innovative activities and the speed of converting activities with very high implementation methods. SMEs are often more agile, innovative, and adaptive than larger organizations. Through funding programs like Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe, the EU seeks to harness these qualities to drive technological advancements and enhance the region’s global competitiveness.
- Regional Development: SMEs widely dispersed across the EU, including in less-developed regions. Supporting these enterprises helps ensure a more balanced and inclusive economic development across the entire European territory.
- Resource Allocation: SMEs help to allocate resources and make resources to be allocated in a more efficient way. This means minimum resources are used to the maximum production or current production done with minimum resources.
- Fair Income Distribution and Poverty Reduction: SMEs play an important role in creating jobs, employing people, creating opportunities for low-income families and women, and reducing poverty. SMEs play effective role in the fair distribution of income.
- Inequality Reduction and Establishing Dynamic Economic Systems: These types of enterprises support the development and dissemination of entrepreneurial skills, and the reason for that is the geographical dispersion of this category of enterprises compared to large enterprises. This prevents economic inequality between urban and rural areas and reduces inequality. For this reason, we can say that these enterprises help governments to attract resources more efficiently. In addition they play an effective role in establishing dynamic and resilient economic systems.
- Employment Creation: One of the important goals of forming and activating SMEs is to create sustainable employment and combat unemployment. The conducted studies show that SMEs have different behavior in creating employment compared to large enterprises, and these differences are:
- The employment flow in small companies is more than in large companies.
- The employment flow in small companies has a relatively stable trend compared to large companies.
- During a recession, small companies create more stable employment than large companies.
Figure 1 shows the comparison of EU employment in small and medium companies and large companies. As we can see, in 2020 micro and small-sized enterprises alone created more employment than large-sized enterprises. The total employment in SMEs is 64.2%. That is a high rate compared to the that rate in large-sized enterprises (35.7%).
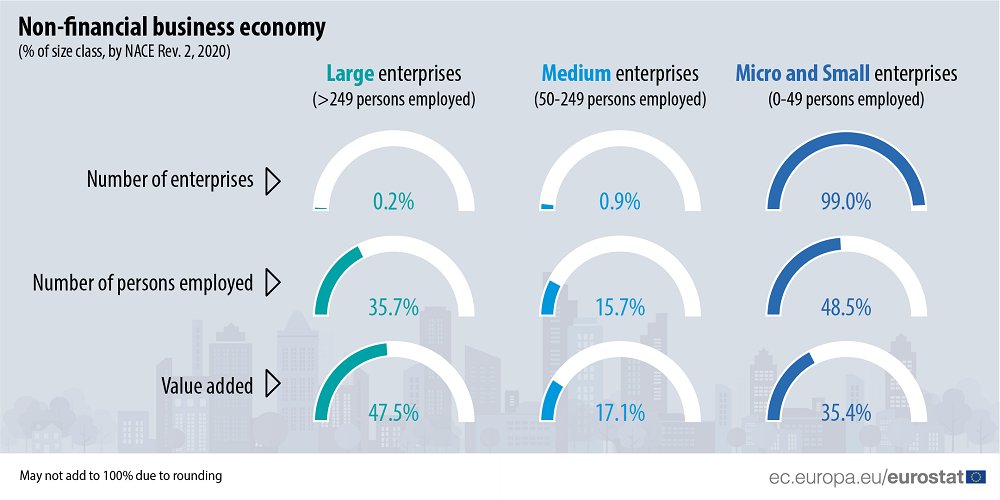
We can also see the added value created by SMEs (52,5%) that this amount is more than large companies (47,5%).
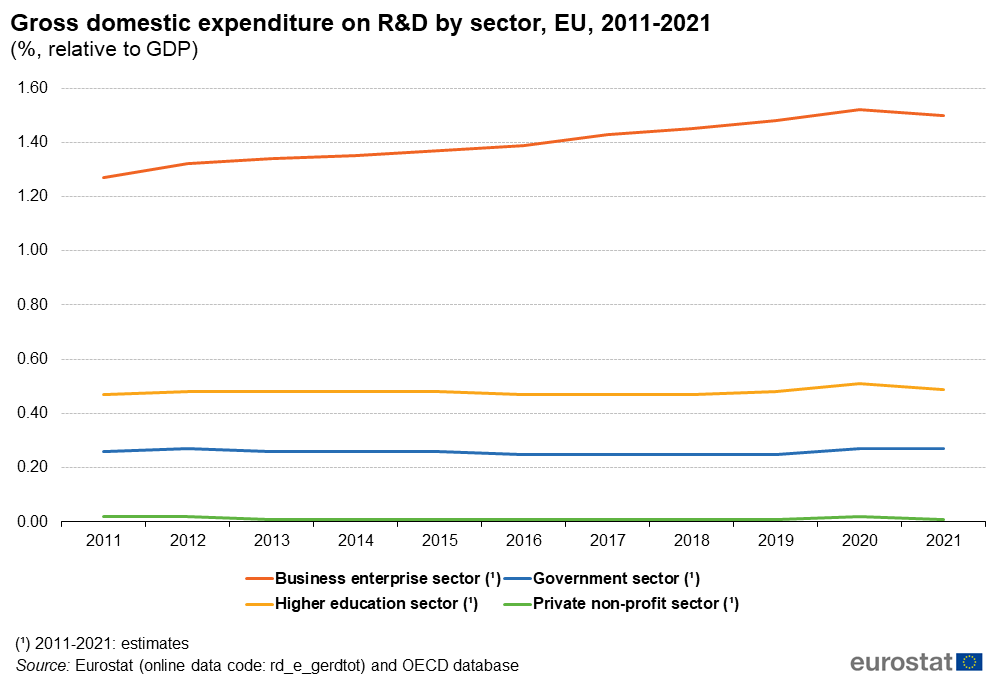
Because of SMEs economic roles, generally support programs provided to these enterprises are more than higher education institutions in the EU. Figure 2 shows the share of research and development expenditures in different sectors in EU countries between the years 2011-2021. As we see in the figure, research and development expenditures in higher education sectors are constant in the years discussed. But these expenditures in commercial enterprises increase over the period. In addition, enterprises have the highest level of R&D expenditures compared to other sectors.
Review of Support Programs for R&D Activities
Research and innovation is one of the important priorities of Europe to realize their political goals, such as ensuring a sustainable and inclusive future for people and the planet. Therefore, cooperation in the field of research and innovation is one of the most central issues in the relations between the EU and other countries. Therefore, European governments design and implement various programs to support these companies, especially SMEs with high technology. This emphasize the SMEs role in EU Funding Policy. The European Commission provides access to financial resources through local financial institutions in EU countries. Different types of financing include loans, micro financing, guarantees, investment and participation through venture capital funds or business angels. These supports have several advantages such as reducing the interest rate, increasing the ceiling of financial provision or laxity in collateral. The main support programs follows as below:
- Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe: Horizon 2020 was the largest research and innovation program in the EU. It was presented with a budget of 80 billion euros over 7 years (2014 to 2020). It aimed attracting private investment and benefiting from pure ideas from the laboratory to the market. In the Horizon 2020 program, special attention was paid to SMEs. Helping to introduce the new ideas of these companies to the market and then helping to further develop these ideas were among the important points of the program in the field of SMEs. After the end of the Horizon 2020 period, the EU research support program entitled Horizon Europe from 2021 to 2027. This program started its work with more than 95.5 billion euros as the largest support program in the world.
- Competitiveness of Enterprises and Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (COSME): This program aims to facilitate the access of SMEs to financial resources in all phases of the enterprise’s life cycle (creation, expansion or transfer of business). In the framework of this program, while providing easier access to guarantees, loans and capital for businesses, financial support from the EU is provided through local financial institutions in member countries.
- EU Finance for innovators (InnovFin): The European Investment Bank Group (EIB and EIF) and European Commission’s collaborative solution was in the form of the Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. InnovFin includes an integrated and complementary set of financial instruments and advisory services covering the entire research and innovation value chain.
- European Fund for Strategic Investments (EFSI): This fund creates the cornerstone of the European Investment Plan. It has a €5.5 billion “SME Window” that provides loans or guarantees to SMEs through the EIF. Also, through EFSI, it is possible to participate with the private sector and venture capital on potential innovative and growing companies. Also providing loans to high-risk SMEs (active in the field of research and innovation or social activities) is possible. These supports go beyond the services of the EIF or other EU financial instruments.
- EU Program for Employment and Social Innovation (EaSI): EsSI is financing tool at EU level to encourage quality and sustainable employment. It also ensure social inclusion, fight poverty and improve working conditions. The vulnerable groups, small enterprises and social enterprises form the target group. In the form of this program, small loans up to 25,000 euros are provided for small enterprises and vulnerable groups who want to start or develop a small company. Also, investments up to 500,000 euros made in social enterprises.
- European Innovation Council (EIC): This program designed in the framework of Horizon 2020 programs. EIC is Europe’s flagship program to identify, develop and scale up breakthrough technologies and innovations. Various financing, investment, business acceleration plans relying on consulting and training services to support innovative and active companies in the field of breakthrough technologies.
- Cultural and Creative Sectors Guarantee Facility (CCS GF): In the form of the “Creative Europe” program, guarantees are provided to financial intermediaries. This provide the necessary financial resources for cultural and creative sector programs. This program supports creative enterprises with loans and other financial instruments. Also, in this program, financial intermediaries are trained to better understand the needs of cultural and creative projects.
Among the introduced support programs, the most comprehensive and complete programs are Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe.
Why Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe Prioritize SMEs?
Horizon 2020 (2014-2020) and its successor, Horizon Europe (2021-2027), are the EU’s main funding programs for R&D. A significant portion of their budget is dedicated to projects that are close to the market and particularly relevant to SMEs. Therefore the SMEs role in EU funding policy is important. The major reasons for this strategy include:
- Commercialization of Research: The ‘Innovation in SMEs’ initiative under Horizon 2020 and the European Innovation Council (EIC) in Horizon Europe aim to help SMEs bring innovative ideas to the market. This encourages the translation of research into practical applications, fostering a more innovative and resilient economy.
- Cross-Border Collaborations: These programs promote collaborations between SMEs, research institutions, and other stakeholders from different EU countries, supporting the exchange of knowledge and the creation of a single European Research Area.
- Addressing Societal Challenges: Both programs focus on societal challenges, such as climate change, health, and clean energy. By funding relevant SME-led projects, the EU leverages the creativity and innovation of these enterprises to tackle pressing societal issues.
Read more about EU public funding and its evaluation here.
Impact of R&D Investment on Sustainability and Well-being
Investing in SME-led R&D has significant impacts on sustainability and the well-being of European citizens:
- Sustainable Development: Many funded projects align with the EU’s goals for sustainable development. For instance, innovative SMEs can contribute to the Green Deal, Europe’s plan to become the first climate-neutral continent by 2050, by developing clean technologies and circular business models.
- Job Creation: Increased R&D funding leads to job creation, both directly within funded SMEs and indirectly through the development of new sectors and markets. This contributes to economic security and improved quality of life for EU citizens.
- Health and Safety: R&D investment can lead to breakthroughs in areas like healthcare, food safety, and security – all of which have a direct impact on citizens’ well-being.
- Resilient Economy: A robust and innovative SME sector supported by R&D funding contributes to a more resilient and diverse economy, better equipped to withstand future shocks.
While the exact statistics may vary, the trends and rationales presented are based on the most recent data available. For the most accurate and up-to-date information, I recommend visiting the European Commission’s website. One can also visit the official pages for Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe.
Future Outlook and Conclusion
The EU continues to advance its agenda on sustainable growth and citizen well-being. So the SMEs role in EU Funding Policy, supported by programs like Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe, will remain central. These programs are expected to:
- Drive Sustainable Innovation: Horizon Europe, with its increased focus on the European Green Deal and the digital transition, will further incentivize SMEs to develop solutions that address these key areas.
- Boost Economic Recovery: Following the economic shock induced by the COVID-19 pandemic, the support for SMEs becomes even more critical. SMEs are key drivers of job creation and economic recovery. So their resilience will help the EU bounce back more robustly.
- Encourage International Cooperation: The EU aims to strengthen international R&D cooperation under Horizon Europe. This will expose SMEs to a wider range of opportunities and collaborations, enhancing their potential for innovation and growth.
The emphasis on SMEs in European funding programs is a strategic move. It bolsters innovation, drives economic growth, and promotes sustainable development. As we look to the future, the continued support for SME-led R&D will remain a cornerstone of the EU’s strategy for a resilient, sustainable, and inclusive economy.

