

Cademix Institute of Technology
Job seekers Portal for Career Acceleration, Continuing Education, European Job Market
Quality Assurance & Quality Control
By: Jewel Antony, Associate Researcher with Cademix & Mechanical Engineer & QA/QC Expert
“Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of high intention, sincere effort, intelligent direction and skillful execution; it represents the wise choice of many alternatives.” ~William A. Foster

Quality assurance (QA ) and quality control (QC) are two terms that are frequently used synonymously used in the industry. Although similar, there are distinct differences between these two definitions. In this article, we explain them with an emphasize on the differences between quality control and quality management. We also provide definitions and examples of each from our own experiences and previous works.
Quality Assurance ( QA) refers to the process used to create deliverables. Usually manager, a client, or even a third party reviewer can do it. Examples of quality assurance include process checklists, project audits and methodology and the development of standards.
Quality Control ( QC) refers to quality related activities related to the creation of project deliverables. Therefore, quality control is used to verify that the deliverables are of acceptable quality and are complete and correct. Some Examples of quality control activities include inspection, peer review and testing.
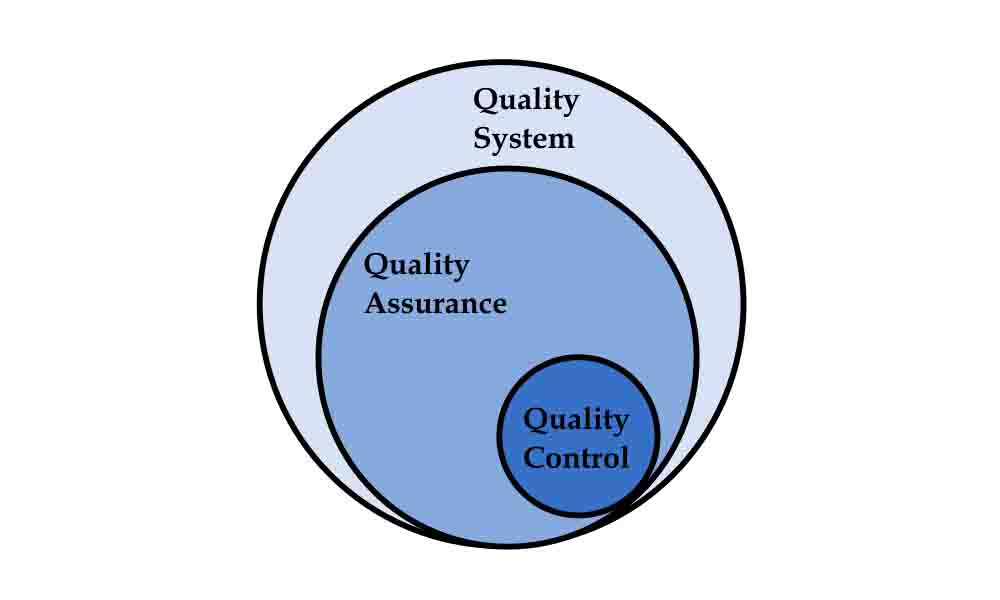
Schematic relationship of quality system, quality assurance and quality control
Quality Assurance
In the context of the technology and industrial systems, we describe the Quality assurance as a quality management component based on providing certainty and confidence that quality standards will be met. The certainty that quality assurance provides has two dimensions. First one is internally to management. The second one is externally and to the consumers, government agencies, regulators, certifiers, and third parties. An alternative definition of quality assurance is that all planned and systematic activities carried out meets the quality requirements.
QA refers to having well-defined best procedures and processes implemented. It’s a consistency method which is also constructive. It’s the task of managers to organize the process of quality assurance. Quality assurance also focuses on the process checklists, process requirements, project evaluations, implementation methods and procedures. From the cause and diagnosis perspective, it is a preventive technique, which aims to determine the appropriate methodology and standards in order to provide the product being produced with a quality conducive setting. Quality assurance is a process-based approach; its primary goal is to prevent, at the planning level, finding defects in deliverables in order to avoid rework, which is often very expensive.
Quality Assurance is a proactive process. It stresses the preparation, documentation and finalization of the standards that are needed to ensure the quality. It helps to understand the specifications and expectations of the company, and this process starts even before the project starts.
Quality Control
We define Quality control as a part of quality management. It focuses on meeting quality requirements. While quality assurance relates to how a process is performed or how a product is made, the quality control is more the inspection aspect of quality management. An alternate definition is the operational techniques and activities used to fulfill requirements for quality. The most important and respected definition of quality is given by Mr. Philip B. Crosby. He says that quality is “Conformance to requirements.”
According to ISO 8402:1996 (Quality Management and Quality Assurance Vocabulary standard), “Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.” According to ISO 9000:2000 (Set of International Quality Standards and Guidelines for Quality Management Systems), “Quality is the degree to which a set of inherent (existing) characteristics fulfills requirements.” To make it simple, we can say that quality is about meeting the customers’ requirements and the deliverable being fit for use. If a product meets or exceeds customers’ requirements you can say that the product is of high quality. However, if it is not meeting its stated requirements the product is of low quality. Keep in mind that, regardless of the grade, the quality should be high. In any case the quality cannot be compromised
“Almost all quality improvement comes via simplification of design, manufacturing… layout, processes, and procedures.” ~Tom Peters
Tools Used in the Quality Assurance Process
In Quality Management, the following tools are used: quality audit, process analysis , quality management, and control tools. A team of external experts comes in for a quality audit to review the process and procedures. When there are some inconsistencies, they may recommend corrective actions, and they will recommend that the procedure change. Quality audit is a great tool for ensuring the project follows best practices and procedures approved.
In process analysis, you evaluate the root cause of any issues and classify any non-value – added activities to find any changes. Tools for quality management and control provide different diagrammatic strategies that help you find solutions, make decisions and prioritize problems. Several examples of these methods include an affinity diagram, tree diagram, network diagram, and so on.
Tools Used in the Quality Control Process
There are usually three Quality Control System strategies. They are testing, statistical analysis and they are the seven simple standard methods. During an inspection, the deliverable is physically inspected for any flaws and tested to see if it corresponds to the specifications. You select a random number of items from a batch in statistical sampling, and inspect them for any defects and conformance. Scatter map, graph chart , histogram, checklist, Pareto diagram, cause-and – effect analysis, and flowchart are the seven common quality methods. These methods help to distinguish flaws and the causes of defects.
The Benefits of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
The following are a few benefits of these processes:
- They provide you with high-quality output and eliminate waste.
- They increase the efficiency of operations.
- They provide customer satisfaction, which helps your brand and helps in growing your business.
- Less rework and after-sale support are required, which will help you save a lot of money.
- They encourage a high level of confidence and a motivated team.
Quality assurance and quality control are closely related, and they have the same objective, i.e., to deliver a defect-free product. Both processes are an integral part of a quality management plan and failure to apply either of them will result in a low-quality product.
Six sigma in Quality control and Quality Assurance
Six Sigma can be a useful tool for companies wanting to control the defects and variations in their processes. This means also implementing excellent quality control. Come along as we learn how quality control can help provide products with the highest quality possible. Much like your basic quality control program, Six Sigma quality control works to find errors and identify areas that need improvement to enhance the quality of products. But, six sigma quality control uses a variety of tools and statistics to not only find the problem quickly, but also to fix it and continue to monitor it. Controlling problems produces higher customer satisfaction and can reduce unnecessary costs for a company. When Six Sigma quality control programs are functioning at their best, they create the highest level of product quality while still meeting goals and objectives.
The goal in any Six Sigma project is to identify and eliminate any defects that are causing variations in quality by defining a sequence of steps around a certain target. The most common example you’ll find use the targets “smaller is better, larger is better or nominal is best.”
- Smaller is better creates an upper specification limit such as having a target of zero for defects or rejected parts.
- Larger is better involves a lower specification limit such as test scores — where the target is 100 percent.
- Nominal is better looks at the middle ground — a customer service rep needs to spend enough time on the phone to troubleshoot a problem, but not so long that they lose productivity.
The process aims to bring data and statistics into the mesh to help objectively identify errors and defects that will impact quality. It’s designed to fit a variety of business goals, allowing organizations to define objectives around specific industry needs.
Diesel and petrol generator manufacturing company
The generator manufacturer industry in India is operated by several large manufacturers and a huge number of smaller manufacturers. They manufacture quality generators of varying sizes in compliance with Indian and international standards. These include ISO 8528 for generating set, ISO 10000 (naturally aspirated) for engines, BS 5514 for reciprocating internal combustion engines, IS, IP and IEC standards for alternators, IS and ISO standards for acoustic enclosures and IS and ISO standards for acoustic enclosures and IS and ISO standards for control/AMF panels. Besides, they also comply with notifications and guidelines issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in regard to various parameters including noise and emission. These manufacturers invest heavily in setting up state-of-the-art facilities for the production of high-quality generators. The two main types of generators produced include diesel generators and gas-based generators. Off late, manufacturers have shown interest in manufacturing hybrid generators that depend on both solar and fuel energy.
The production of generators generally falls into categories based on KVA Ratings mentioned below:
- 5 KVA – 75 KVA
- 75.1 KVA – 375 KVA
- 375.1 KVA – 750 KVA
- 750.1 KVA – 1,000 KVA
- 1,000.1 KVA – 2,000 KV
- Above 2,000 KVA
I Have worked as Graduate Engineering Trainee in various departments such as production, maintaice and Quality.
Production
-coupling
-Assembling
-Testing
-PDI (predelivery inspection)
Maintaince
- Lubrication Service. The engine oil must be checked while shutting down the generator at regular intervals using a dipstick. …
- Cooling System. …
- Fuel System. …
- Testing Batteries. …
- Routine Engine Exercise. …
- Diesel Generator Clean. …
- Exhaust system inspection
Quality
- Acquiring raw materials.
- Purchasing third-party components and sub-assemblies.
- Designing and using inspection procedure
- Complying with production processes.
- Responding to defects.
Off-loading
- Use mobile crane to off-load the Generator sets. Capacity of crane shall be capable to carry the weight of the generator set. All safety precaution shall be adhered during off loading.
- Ensure the safety of Equipment’s and workers.
- Off load the Generator sets on the designated offloading area, make sure the Generator set will seat on pipe rollers or wooden flanks.
- If the Generator Room is not ready for generator set installation, proper protection of Generator set shall be provided and cover it.
Pre-Installation
- All materials and documentation relevant to the particular section of works shall be checked prior to the installation.
- Make sure that the access for generator set installation is free from obstructions.
- Make sure that supporting flanks, pipe rollers,chian blocks,hydraulic jacks and other tools required for installation are in place.

Installation:
- Lift the Generator using mobile crane or portable hydraulic crocodile jack. Place pipe rollers under the generator skid. Make sure that the pipe rollers are properly set to the direction of generator position.
- Where in a generator set cross a trench or unequal elevation, use steel channels or I-beam are properly supported to carry the weight of the Generator set.
- Set the generator set it proper location. Lift the generator set using portable crocodile hydraulic jack and let it sit on elevated flanks or l-beams.
- Fix the spring vibration isolator. Ensure that it fixed and aligned properly.
- Lift the generator set and install the spring vibration isolator. Bolt and tight properly the generator.
- After completing all associated works related to generator set, raise a request for inspection for Generator installation.
Quality commissioning
- Test the generator in accordance to specification and manufacturer recommendation.
- All Testing will be carried out in the presence of consultant.
- Test shall be carried out by the manufactures testing engineers.
- All Test sheet shall be certified by the manufacturer representative.

References
Usmani, F., 2020. Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control | PM Study Circle. [online] PM Study Circle. Available at: <https://pmstudycircle.com/2012/01/quality-assurance-vs-quality-control/> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Asq.org. 2020. Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: Definitions & Differences | ASQ. [online] Available at: <https://asq.org/quality-resources/quality-assurance-vs-control> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Zrymiak, D., 2015. The Certified Quality Improvement Associate Handbook, third edition. Quality Management Journal, 22(2), pp.61-63.
Study.com. 2020. [online] Available at: <https://study.com/academy/lesson/six-sigma-quality-control-improvement.html> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Scribd. 2020. 00 – MS – Diesel Generator Installation.Docx | Quality Assurance | Specification (Technical Standard). [online] Available at: <https://www.scribd.com/document/424444248/00-MS-Diesel-Generator-Installation-docx> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Guru99.com. 2020. Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: What’s The Difference?. [online] Available at: <https://www.guru99.com/quality-assurance-vs-quality-control.html> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
People also visited:
Quality Assurance & Quality Control
By: Jewel Antony, Associate Researcher with Cademix & Mechanical Engineer & QA/QC Expert
“Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of high intention, sincere effort, intelligent direction and skillful execution; it represents the wise choice of many alternatives.” ~William A. Foster

Quality assurance (QA ) and quality control (QC) are two terms that are frequently used synonymously used in the industry. Although similar, there are distinct differences between these two definitions. In this article, we explain them with an emphasize on the differences between quality control and quality management. We also provide definitions and examples of each from our own experiences and previous works.
Quality Assurance ( QA) refers to the process used to create deliverables. Usually manager, a client, or even a third party reviewer can do it. Examples of quality assurance include process checklists, project audits and methodology and the development of standards.
Quality Control ( QC) refers to quality related activities related to the creation of project deliverables. Therefore, quality control is used to verify that the deliverables are of acceptable quality and are complete and correct. Some Examples of quality control activities include inspection, peer review and testing.

Schematic relationship of quality system, quality assurance and quality control
Quality Assurance
In the context of the technology and industrial systems, we describe the Quality assurance as a quality management component based on providing certainty and confidence that quality standards will be met. The certainty that quality assurance provides has two dimensions. First one is internally to management. The second one is externally and to the consumers, government agencies, regulators, certifiers, and third parties. An alternative definition of quality assurance is that all planned and systematic activities carried out meets the quality requirements.
QA refers to having well-defined best procedures and processes implemented. It’s a consistency method which is also constructive. It’s the task of managers to organize the process of quality assurance. Quality assurance also focuses on the process checklists, process requirements, project evaluations, implementation methods and procedures. From the cause and diagnosis perspective, it is a preventive technique, which aims to determine the appropriate methodology and standards in order to provide the product being produced with a quality conducive setting. Quality assurance is a process-based approach; its primary goal is to prevent, at the planning level, finding defects in deliverables in order to avoid rework, which is often very expensive.
Quality Assurance is a proactive process. It stresses the preparation, documentation and finalization of the standards that are needed to ensure the quality. It helps to understand the specifications and expectations of the company, and this process starts even before the project starts.
Quality Control
We define Quality control as a part of quality management. It focuses on meeting quality requirements. While quality assurance relates to how a process is performed or how a product is made, the quality control is more the inspection aspect of quality management. An alternate definition is the operational techniques and activities used to fulfill requirements for quality. The most important and respected definition of quality is given by Mr. Philip B. Crosby. He says that quality is “Conformance to requirements.”
According to ISO 8402:1996 (Quality Management and Quality Assurance Vocabulary standard), “Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.” According to ISO 9000:2000 (Set of International Quality Standards and Guidelines for Quality Management Systems), “Quality is the degree to which a set of inherent (existing) characteristics fulfills requirements.” To make it simple, we can say that quality is about meeting the customers’ requirements and the deliverable being fit for use. If a product meets or exceeds customers’ requirements you can say that the product is of high quality. However, if it is not meeting its stated requirements the product is of low quality. Keep in mind that, regardless of the grade, the quality should be high. In any case the quality cannot be compromised
“Almost all quality improvement comes via simplification of design, manufacturing… layout, processes, and procedures.” ~Tom Peters
Tools Used in the Quality Assurance Process
In Quality Management, the following tools are used: quality audit, process analysis , quality management, and control tools. A team of external experts comes in for a quality audit to review the process and procedures. When there are some inconsistencies, they may recommend corrective actions, and they will recommend that the procedure change. Quality audit is a great tool for ensuring the project follows best practices and procedures approved.
In process analysis, you evaluate the root cause of any issues and classify any non-value – added activities to find any changes. Tools for quality management and control provide different diagrammatic strategies that help you find solutions, make decisions and prioritize problems. Several examples of these methods include an affinity diagram, tree diagram, network diagram, and so on.
Tools Used in the Quality Control Process
There are usually three Quality Control System strategies. They are testing, statistical analysis and they are the seven simple standard methods. During an inspection, the deliverable is physically inspected for any flaws and tested to see if it corresponds to the specifications. You select a random number of items from a batch in statistical sampling, and inspect them for any defects and conformance. Scatter map, graph chart , histogram, checklist, Pareto diagram, cause-and – effect analysis, and flowchart are the seven common quality methods. These methods help to distinguish flaws and the causes of defects.
The Benefits of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
The following are a few benefits of these processes:
- They provide you with high-quality output and eliminate waste.
- They increase the efficiency of operations.
- They provide customer satisfaction, which helps your brand and helps in growing your business.
- Less rework and after-sale support are required, which will help you save a lot of money.
- They encourage a high level of confidence and a motivated team.
Quality assurance and quality control are closely related, and they have the same objective, i.e., to deliver a defect-free product. Both processes are an integral part of a quality management plan and failure to apply either of them will result in a low-quality product.
Six sigma in Quality control and Quality Assurance
Six Sigma can be a useful tool for companies wanting to control the defects and variations in their processes. This means also implementing excellent quality control. Come along as we learn how quality control can help provide products with the highest quality possible. Much like your basic quality control program, Six Sigma quality control works to find errors and identify areas that need improvement to enhance the quality of products. But, six sigma quality control uses a variety of tools and statistics to not only find the problem quickly, but also to fix it and continue to monitor it. Controlling problems produces higher customer satisfaction and can reduce unnecessary costs for a company. When Six Sigma quality control programs are functioning at their best, they create the highest level of product quality while still meeting goals and objectives.
The goal in any Six Sigma project is to identify and eliminate any defects that are causing variations in quality by defining a sequence of steps around a certain target. The most common example you’ll find use the targets “smaller is better, larger is better or nominal is best.”
- Smaller is better creates an upper specification limit such as having a target of zero for defects or rejected parts.
- Larger is better involves a lower specification limit such as test scores — where the target is 100 percent.
- Nominal is better looks at the middle ground — a customer service rep needs to spend enough time on the phone to troubleshoot a problem, but not so long that they lose productivity.
The process aims to bring data and statistics into the mesh to help objectively identify errors and defects that will impact quality. It’s designed to fit a variety of business goals, allowing organizations to define objectives around specific industry needs.
Diesel and petrol generator manufacturing company
The generator manufacturer industry in India is operated by several large manufacturers and a huge number of smaller manufacturers. They manufacture quality generators of varying sizes in compliance with Indian and international standards. These include ISO 8528 for generating set, ISO 10000 (naturally aspirated) for engines, BS 5514 for reciprocating internal combustion engines, IS, IP and IEC standards for alternators, IS and ISO standards for acoustic enclosures and IS and ISO standards for acoustic enclosures and IS and ISO standards for control/AMF panels. Besides, they also comply with notifications and guidelines issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in regard to various parameters including noise and emission. These manufacturers invest heavily in setting up state-of-the-art facilities for the production of high-quality generators. The two main types of generators produced include diesel generators and gas-based generators. Off late, manufacturers have shown interest in manufacturing hybrid generators that depend on both solar and fuel energy.
The production of generators generally falls into categories based on KVA Ratings mentioned below:
- 5 KVA – 75 KVA
- 75.1 KVA – 375 KVA
- 375.1 KVA – 750 KVA
- 750.1 KVA – 1,000 KVA
- 1,000.1 KVA – 2,000 KV
- Above 2,000 KVA
I Have worked as Graduate Engineering Trainee in various departments such as production, maintaice and Quality.
Production
-coupling
-Assembling
-Testing
-PDI (predelivery inspection)
Maintaince
- Lubrication Service. The engine oil must be checked while shutting down the generator at regular intervals using a dipstick. …
- Cooling System. …
- Fuel System. …
- Testing Batteries. …
- Routine Engine Exercise. …
- Diesel Generator Clean. …
- Exhaust system inspection
Quality
- Acquiring raw materials.
- Purchasing third-party components and sub-assemblies.
- Designing and using inspection procedure
- Complying with production processes.
- Responding to defects.
Off-loading
- Use mobile crane to off-load the Generator sets. Capacity of crane shall be capable to carry the weight of the generator set. All safety precaution shall be adhered during off loading.
- Ensure the safety of Equipment’s and workers.
- Off load the Generator sets on the designated offloading area, make sure the Generator set will seat on pipe rollers or wooden flanks.
- If the Generator Room is not ready for generator set installation, proper protection of Generator set shall be provided and cover it.
Pre-Installation
- All materials and documentation relevant to the particular section of works shall be checked prior to the installation.
- Make sure that the access for generator set installation is free from obstructions.
- Make sure that supporting flanks, pipe rollers,chian blocks,hydraulic jacks and other tools required for installation are in place.

Installation:
- Lift the Generator using mobile crane or portable hydraulic crocodile jack. Place pipe rollers under the generator skid. Make sure that the pipe rollers are properly set to the direction of generator position.
- Where in a generator set cross a trench or unequal elevation, use steel channels or I-beam are properly supported to carry the weight of the Generator set.
- Set the generator set it proper location. Lift the generator set using portable crocodile hydraulic jack and let it sit on elevated flanks or l-beams.
- Fix the spring vibration isolator. Ensure that it fixed and aligned properly.
- Lift the generator set and install the spring vibration isolator. Bolt and tight properly the generator.
- After completing all associated works related to generator set, raise a request for inspection for Generator installation.
Quality commissioning
- Test the generator in accordance to specification and manufacturer recommendation.
- All Testing will be carried out in the presence of consultant.
- Test shall be carried out by the manufactures testing engineers.
- All Test sheet shall be certified by the manufacturer representative.

References
Usmani, F., 2020. Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control | PM Study Circle. [online] PM Study Circle. Available at: <https://pmstudycircle.com/2012/01/quality-assurance-vs-quality-control/> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Asq.org. 2020. Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: Definitions & Differences | ASQ. [online] Available at: <https://asq.org/quality-resources/quality-assurance-vs-control> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Zrymiak, D., 2015. The Certified Quality Improvement Associate Handbook, third edition. Quality Management Journal, 22(2), pp.61-63.
Study.com. 2020. [online] Available at: <https://study.com/academy/lesson/six-sigma-quality-control-improvement.html> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Scribd. 2020. 00 – MS – Diesel Generator Installation.Docx | Quality Assurance | Specification (Technical Standard). [online] Available at: <https://www.scribd.com/document/424444248/00-MS-Diesel-Generator-Installation-docx> [Accessed 30 April 2020].
Guru99.com. 2020. Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control: What’s The Difference?. [online] Available at: <https://www.guru99.com/quality-assurance-vs-quality-control.html> [Accessed 30 April 2020].